Na K Atpase Pump Action Potential
This pump is called a P-type ion pump because the ATP interactions. What happens if you keep firing action potentials and dont have the NaK pump to reset the Na levels to where they should be.
Neurons need the Na K ATPase pump to reverse postsynaptic sodium flux to re-establish the potassium and sodium gradients which arenecessary to fire action potentials.

Na k atpase pump action potential. The voltage-gated Na channel actually has two gates. Furthermore it is important to note that this pump is electrogenic in nature because it extrudes 3 Na for every 2 K entering the cell. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy.
Nov 22 2012 THE RESTING POTENTIAL-THE NA-K ATPASE PUMPMechanism PDB ID 2B8E 2ZKE biological assembly K K Unphosphorylated form binds 3 intracellular Na ions while binding ATP Hydrolysis of ATP ADP Phosphorylation of the pump at a highly conserved Aspartate residue. Na K -ATPase hydrolyses ATP to pump 3 Na ions out and 2 K into cells. The NaK-ATPase pump helps to maintain osmotic equilibrium and membrane potential in cells.
The activity of the NaK-pump also influences the membrane potential directly by generating an outward sodium current that is larger when the NaK-pump activity is greater. When an enzyme in the pump called sodium-potassium-ATPase splits the phosphate from the ADP the energy released powers the transport action of the pump. Thus the maintenance of a normal electrical function requires that the NaK-pump maintain normal ionic concentrations within the cell.
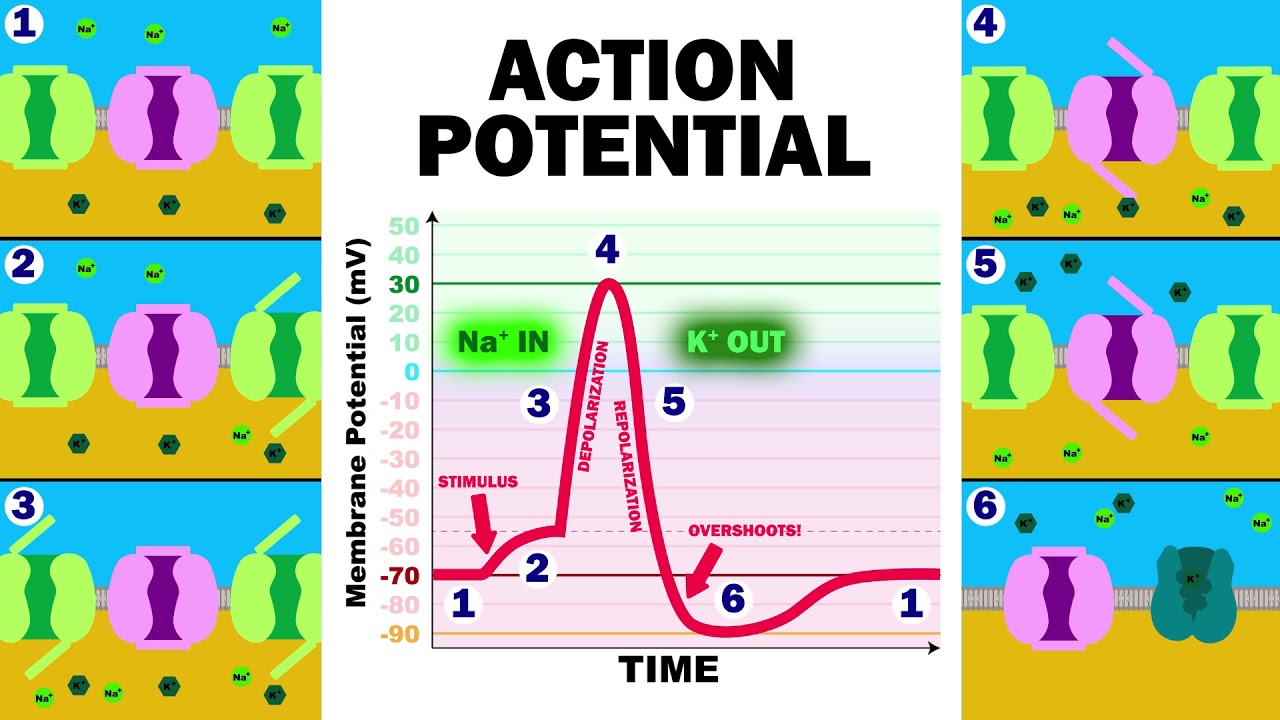
Mar 06 2013 As we have seen the depolarization and repolarization of an action potential are dependent on two types of channels the voltage-gated Na channel and the voltage-gated K channel. The activity of the NaK-pump is regulated by several factors including the intracellular sodium concentration and the neuromediators norepinephrine and acetylcholine. Mar 28 2007 The purpose of the NaK pump is to push 3 Na out and 2 K in to maintain the cell potential.
By pumping more positive changes out of the cell than into the cell the pump activity. This causes depolarization of the resting membrane potential as predicted by the Nernst equation primarily because of the reduction in the potassium concentration gradient across the cell membrane. It accomplishes the transport of three Na to the outside of the cell and the transport of two K ions to the inside.
The Na K-ATPase pump maintains the gradient of a higher concentration of sodium extracellularly and a higher level of potassium intracellularly. This unbalanced charge transfer contributes to the separation of charge across the membrane. On the extracellular side it is stimulated by K Km 0515 mM.
The sodium-potassium pump sets the membrane potential of the neuron by keeping the concentrations of Na and K at constant. It regulates the osmolarityof the cytosolby controlling the solute concentration inside the cellThe main function of the NK ATPase pump is to maintain resting potential so that the cells will be keeping in a state of a low concentration of sodium ions and high levels of potassium ions within the cell intracellular. The sodium-potassium pump 3A3Y from Squalus acanthias is an ATPase crucial to maintaining the concentration gradient and action potential across the plasma membrane.
The sodium-potassium pump is an important contributer to action potential produced by nerve cells. Since this occurs at well-below the Vmax in intact cells any increase in intracellular Na increases activity. Astrocytes also need Na K ATPase pump to maintain the sodium gradient as the sodium gradient maintains neurotransmitter reuptake.
Jun 06 2017 Not least the brain has a massive demand for NaK-ATPase activity since neurons rely on the pump to reverse postsynaptic sodium flux to reestablish the sodium and potassium gradients used to fire action potentials and in astrocytes the sodium gradient drives neurotransmitter reuptake. A special feature of the Na-K ATPase pump is that its degree of activity is strongly stimulated when excess sodium ions accumulate inside the cell membrane. Aug 22 2020 The brain also requires NA K ATPase activity.
One is the activation gate which opens when the membrane potential crosses -55 mV. 2 23 Digitalis more commonly known as foxglove is known to have a large effect on the NaK ATPase ultimately causing a more forceful contraction of the heart. It is stimulated by Na.
Part 4 in a 8 part lecture on the ACTION POTENTIAL in a flipped Human Physiology course taught by Wendy Riggs. ADP Pi Phosphorylated form has a low affinity for Na Release Pump. Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
In 1969 a group led by PF Baker that was experimenting using squid axons published a finding that proposed that there exists a means of Na exit from cells other than the sodium-potassium pump. This protein pump catalyzes the exchange of three sodium ions for two potassium ions against their concentration gradients by hydrolyzing ATP. The sodium and potassium move against the concentration gradients.
Watch the whole lecture all 8 videos. The activity of the NaK-pump influences the membrane potential directly and indirectly. Too much Na buildup inside the cell.
In fact the pumping activity increases approximately in proportion to the third power of this intracellular sodium concentration.

Scheme Of The Insertion Of Na K Atpase Into The Plasma Membrane Ionic Download Scientific Diagram
Komentar
Posting Komentar